Showing posts with label C#. Show all posts
how to implement polymorphism in C-#(SHARP) application
Polymorphism is one of the most impotent feature of OOP that is used to exhibit different form of any particular procedure. With the help of polymorphism , you can use one procedure as many whys as per your requirement.
let's consider it with an example :
you can make a procedure for calculating the area of geometrical figure and can calculate the are of circle , triangle , or rectangle with same procedure and different parameters for each geometrical figure.
the advantages of polymorphism are as follow:
let's consider it with an example :
you can make a procedure for calculating the area of geometrical figure and can calculate the are of circle , triangle , or rectangle with same procedure and different parameters for each geometrical figure.
the advantages of polymorphism are as follow:
- Allow you to invoke methods of a derived class through base class reference during runtime.
- Provide different implementation of method in a class that are called through the same name.
basic syntax :
class baseclass
{
public void basemethod()
{
// method body
}
}
class derivedclass : baseclass
{
public void derivedmethod()
{
// method body
}
}
There are two type of polymorphism , which are as follow:
- Static polymorphism / compile time polymorphism / overloading
- Dynamic polymorphism / run time polymorphism / overriding
Compile time polymorphism:
there are the two type of compile time polymorphism
- method overloading:
- operator overloading:
method overloading: Method overloading is a concept in which a method behaves according to the number and type of parameters passed to it. In method overloading , you can define many method with the same name but different sing natures. A methods signature is the combination of the method name's , along with the number , type of order of the parameters.
.shoeing the code of method overloading application:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace method_overloading.cs
{
public class shape
{
public void area(int side)
{
int squarera = side * side;
Console.WriteLine("area of squar is:" + squarera);
}
public void area(int lenth, int breadth)
{
int rectanglearea = lenth * breadth;
Console.WriteLine("area of rectangle is:" + rectanglearea);
}
public double area(double Base, double height)
{
double trianglearea = (Base * height) / 2;
Console.WriteLine("the area of triange is:" + trianglearea);
return trianglearea;
}
public void area(double radius)
{
double circlearea = 3.14 * radius * radius;
Console.WriteLine("the area of circle is:" + circlearea);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
shape Shape = new shape();
Shape.area(10);
Shape.area(10,10);
Shape.area(10.10,10.10);
Shape.area(10.00);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
operator overloading: We know that , all the operator have specified meaning and functionality , such as the + (plus) operator add two numbers and - ( minus) operator subtract two number. However , you can change the functionality of an operator by using overloading them.When overload an operator , you need to create a method that must be preceded by operator keyword.
showing the code for operator overloading application:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace operator_overloading.cs
{
class uninaryoperator
{
private int Number1, Number2;
public uninaryoperator()
{
}
public uninaryoperator(int number1, int number2)
{
Number1 = number1;
Number2 = number2;
}
public void showdata()
{
Console.WriteLine("the number are :" + Number1 + "and" + Number2);
}
public static uninaryoperator operator -(uninaryoperator opr)
{
uninaryoperator obj = new uninaryoperator();
obj.Number1 = -opr.Number1;
obj.Number2 = -opr.Number2;
return obj;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
uninaryoperator opr1 = new uninaryoperator(20,30);
Console.WriteLine("before operatore ovrloading");
opr1.showdata();
uninaryoperator opr2 = new uninaryoperator();
opr2 = -opr1;
Console.WriteLine("==============================================");
Console.WriteLine("after operator overloading");
opr2.showdata();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Runtime polymorphism / overriding: override is a feature that allow a derived class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already define in a base class. The implementation of a derived class override or replace the implementation of method in a base class. This feature is also known as "runtime polymorphism".
To invoke the method of a derived class that is already define in a base class , you need to perform the following steps.............
- declare the base class method as "virtual"
- Implement the derived class method using the "override" keyword.
basic syntax:
class baseclass
{
public virtual void showdata()
{
// method body
}
}
class derivedclass : baseclass
public override void showdata()
{
// method body
}
showing the code of runtime polymorphism:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace overloading.cs
{
class person
{
private int fage;
public person()
{
fage = 21;
}
public virtual void setage(int age)
{
fage = age;
}
public virtual int getage()
{
return fage;
}
}
class adultperson : person
{
public adultperson()
{
}
override public void setage(int age)
{
if (age > 21)
base.setage(age);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
person p = new person();
p.setage(18);
adultperson ad = new adultperson();
ad.setage(18);
Console.WriteLine("person age is :"+ p.getage());
Console.WriteLine("person age is :" + ad.getage());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
how to use inheritance in C-#(SHARP) application
The most important reason to use object oriented programming (OOP's) is that , it's supports INHERITANCE. Inheritance is the property in which through a class derived properties from another class. A class that's inherit the properties of another class is called a child or derived class , whereas , the class from which a child class inherit is called as base or parent class. A parent class is the higher level in class hierarchy.
INHERITANCE IS OF FOUR TYPE , WHICH ARE AS FOLLOW:
single inheritance: In which t , there is only one base class or one derived class. This means that a derived class inherit the properties from single base class.
Hierarchical inheritance: In which , multiple derived class are inherit from single base class.
Multilevel inheritance: In which , a child class is derived from a base class , which is turned is derived from another class.
Multiple inheritance: In which , a child class derived from multiple base class.
showing the code how to impement inheritance in C# application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace inheritance.cs
{
public class baseclass
{
public int datamember;
public void baseclassmode()
{
Console.WriteLine("i am a base class method()");
}
}
public class derivedclass : baseclass
{
public void derivedclassmethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("i am a derived class method()");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// create a base class object..
Console.WriteLine("i am accessing base class object..");
baseclass bc = new baseclass();
bc.datamember = 1;
bc.baseclassmode();
Console.WriteLine("=====================================");
// create a derived class object..
Console.WriteLine("i am accessing derived class object..");
derivedclass dc = new derivedclass();
dc.datamember = 2;
dc.baseclassmode();
dc.derivedclassmethod();
Console.WriteLine("press enter to quit..");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
INHERITANCE IS OF FOUR TYPE , WHICH ARE AS FOLLOW:
single inheritance: In which t , there is only one base class or one derived class. This means that a derived class inherit the properties from single base class.
Hierarchical inheritance: In which , multiple derived class are inherit from single base class.
Multilevel inheritance: In which , a child class is derived from a base class , which is turned is derived from another class.
Multiple inheritance: In which , a child class derived from multiple base class.
showing the code how to impement inheritance in C# application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace inheritance.cs
{
public class baseclass
{
public int datamember;
public void baseclassmode()
{
Console.WriteLine("i am a base class method()");
}
}
public class derivedclass : baseclass
{
public void derivedclassmethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("i am a derived class method()");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// create a base class object..
Console.WriteLine("i am accessing base class object..");
baseclass bc = new baseclass();
bc.datamember = 1;
bc.baseclassmode();
Console.WriteLine("=====================================");
// create a derived class object..
Console.WriteLine("i am accessing derived class object..");
derivedclass dc = new derivedclass();
dc.datamember = 2;
dc.baseclassmode();
dc.derivedclassmethod();
Console.WriteLine("press enter to quit..");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
\
Want to know more about inheritance click here ...
LEARN c-# VALUE TYPE , STRUCT TYPE , AND ENUMERATION TYPE ( CLASS 3 )
value type :
value type are allow you to store the data directly into the variable. They are derived from SYSTEM.VALUETYPE and have a special behavior in Common Language Run-time ( CLR). The value type and their content are stored same location in memory. The default value of value types are stored in stack. int
struct type:
structs types are a special of objects having the properties of value types. As you know that the value types are stored on the stack; inherently the struct types are also stored on the stack.
The structs type encapsulate small group of related variable , such as , the name , rollno , age , class name , and section of a student. They can contain constructor , method , properties , operator , event , nested types , indexers , constant and field. While creating the struct type , you should remember that struct members can not be declared as protected as they fail to support inheritance. Under the struct declaration , the field can be initialized only when they are declared as const or static.
the following code shows how to create "struct type":
public struct student
{
string name;
int rollno;
int classname; // fields
int section;
......... // method
............ , , // properties
}
enumeration type:
Enumeration are the user-defined integer data type that are declared using the enum keyword. Using enumeration , you can defined a set of named integral that can be assigned to a variable.
for example :
Traffic light have three possible states -- the green light indicating go , the yellow light indicating to get prepared to stop , and the red light to indicating to stop. A traffic light have one of these three states at a time , implying that the traffic light can be only red , yellow , and green at a time. In such case , you can defined enumeration type variable and assign three value in it.
the following code shows how to create enumeration type :
enum trafficlight
{ red , green , yellow };
to use enumeration type you need to declared a variable of new enumeration type , as showing in the code :
trafficlight t1;
the trafficlight enumeration can take any of the three values , red, green, and yellow.
t1 = trafficlight.red
t1 = trafficlight.green
t1 = trafficlight.yellow
Enumeration by default , being with the value of 0 for the first entry. However you can modify this value by entering a different value for the first entry , as shown in the code:
enum trafficlight
{
red = 1, green , yellow
}
showing the code for how to use enumeration in C-sharp application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace enumeration.cs
{
public enum color { red = 1, green, yellow };
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("plese select 1 for red 2 for green 3 for yello");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
int colInt = Int32.Parse(str);
color col = (color)colInt;
switch (col)
{
case color.red:
{
Console.WriteLine("the selected color is red..");
}
break;
case color.green:
{
Console.WriteLine("the selected color is green..");
}
break;
case color.yellow:
{
Console.WriteLine("the selected color is yellow..");
}
break;
default:
{
Console.WriteLine("invalid option..");
}
break;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
value type are allow you to store the data directly into the variable. They are derived from SYSTEM.VALUETYPE and have a special behavior in Common Language Run-time ( CLR). The value type and their content are stored same location in memory. The default value of value types are stored in stack. int
struct type:
structs types are a special of objects having the properties of value types. As you know that the value types are stored on the stack; inherently the struct types are also stored on the stack.
The structs type encapsulate small group of related variable , such as , the name , rollno , age , class name , and section of a student. They can contain constructor , method , properties , operator , event , nested types , indexers , constant and field. While creating the struct type , you should remember that struct members can not be declared as protected as they fail to support inheritance. Under the struct declaration , the field can be initialized only when they are declared as const or static.
the following code shows how to create "struct type":
public struct student
{
string name;
int rollno;
int classname; // fields
int section;
......... // method
............ , , // properties
}
enumeration type:
Enumeration are the user-defined integer data type that are declared using the enum keyword. Using enumeration , you can defined a set of named integral that can be assigned to a variable.
for example :
Traffic light have three possible states -- the green light indicating go , the yellow light indicating to get prepared to stop , and the red light to indicating to stop. A traffic light have one of these three states at a time , implying that the traffic light can be only red , yellow , and green at a time. In such case , you can defined enumeration type variable and assign three value in it.
the following code shows how to create enumeration type :
enum trafficlight
{ red , green , yellow };
to use enumeration type you need to declared a variable of new enumeration type , as showing in the code :
trafficlight t1;
the trafficlight enumeration can take any of the three values , red, green, and yellow.
t1 = trafficlight.red
t1 = trafficlight.green
t1 = trafficlight.yellow
Enumeration by default , being with the value of 0 for the first entry. However you can modify this value by entering a different value for the first entry , as shown in the code:
enum trafficlight
{
red = 1, green , yellow
}
showing the code for how to use enumeration in C-sharp application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace enumeration.cs
{
public enum color { red = 1, green, yellow };
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("plese select 1 for red 2 for green 3 for yello");
string str = Console.ReadLine();
int colInt = Int32.Parse(str);
color col = (color)colInt;
switch (col)
{
case color.red:
{
Console.WriteLine("the selected color is red..");
}
break;
case color.green:
{
Console.WriteLine("the selected color is green..");
}
break;
case color.yellow:
{
Console.WriteLine("the selected color is yellow..");
}
break;
default:
{
Console.WriteLine("invalid option..");
}
break;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
LEARN C-SHARP IDENTIFIERS AND KEYWORDS , DATA TYPE , VARIABLES , CONSTANTS ( class 2)
what is identifiers and keywords:
In C# , an identifiers is a sequence of character used in identify the variable , constant , or any user defined programming element. An identifiers starts with a letter or an underscore and end with a character. C# identifiers are case sensitive , which means , the variable names sum , Sum , and SUM all three are different from each other.
you must remember the following rules while creating identifiers:
In C# , an identifiers is a sequence of character used in identify the variable , constant , or any user defined programming element. An identifiers starts with a letter or an underscore and end with a character. C# identifiers are case sensitive , which means , the variable names sum , Sum , and SUM all three are different from each other.
you must remember the following rules while creating identifiers:
- An identifiers must begin either with a letter or underscore.
- An identifiers cane have letter , digits , and underscore.
- An identifiers must not be a reserved word ( keyword in C# ).
- An identifiers must be a complete word without any blank space.
Keyword are the reserved word whose meanings are the predefined to the C# compiler. In other words , keywords are those words , which are the reserved by the C# compiler to be used for the specific task. You can not use keyword as variable , method , and properties because they are already defined to the compiler to perform specific functionalists.
data type , variables and constant:
C# supports a rich and varied selection of data type , from built in types , such as integers , strings , to user-ned types , such as enumeration , structure , and classes.
when declaring with these data types , you must remember the following points :
- All variables , whether user-define or built-in , can be used as object anywhere in a program.
- All variables in a program are automatically initialized to default value by the system when they are declared.
constant :
similar to a variable , a constant is also used to store a values. however , unlike a variable , the value of a constant does not change during the execution of a program. A variable is declared as constant by using const keyword.
the following code shows how to use constant variable in your application:
const double e = 2.78516542;
const int x = 100;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace constant_variables.cs
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
const double pi = 3.17; // declaring a constant variable.
int r;
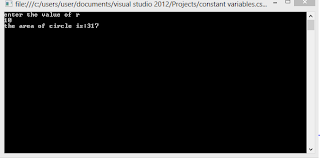
Console.WriteLine("enter the value of r");
r = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
double circlearea = pi * r * r;
Console.WriteLine("the area of circle is:" + circlearea);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
LET'S LEARN C-sharp 5.0 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE ( class 1)
We know that visual c# , commonly known as C#, intermediate programming language use to create executable programs. It's an object-oriented programming language , which is combine of power and efficiency of C++ , simplicity and object-oriented approach of JAVA , and creativeness of VISUAL BASIC. Similar to java , C# does not use the multiple inheritance and pointers but provides the garbage collection at run time.
shows a stander-ed C# application that prints the literal string hello world to the console output window.
In this application , you can see that the entire program is wrapped in the namespace helloworld statement. this namespace contain a class name program , which turn contains a method called main() . The main() method must be declared as static , as it does not require any object foe calling .
run the application by pressing F5 key . the output the application is shown in figure .
Now , let's start the C# by discussing the features of C# .......
flexible : Refers to the capability of C# programs of getting executed on the local system , any remote system or on the web.
powerful : Refers to the ability of C# to create any type of application , such as word processor , spreadsheet , and even compilers for some language .
easy to use : Refers to the use of simpler code statement instead of using complex data types and operators , such as pointers.
visually oriented : Allow you to use the .NET code libraries for developing complicated and attractive interfaces.
let's creating a simple C# 5.0 console application
let's learn to create a C# 5.0 console application named hello-world. To create the hello world application perform the following steps:
before following these steps you need to download the visual studio 2012.
1 >> open visual studio 2012 IDE by selecting start ==> All programs ==> Microsoft visual studio 2012 ==> visual studio 2012
2 >> Select file ==> New project on the menu bar. The new project dialog box opens.
3 >> select installed ==> templates ==> visual C# ==> windows option from the left pane and then select console application template from the middle pane. Enter the name , for instance hello world in the name text box. Enter the location for the application in the location combo box using the browse button , as shown in the figure.
4 >> Click the OK button to create the new console application in visual C#, the visual studio 2012 IDE opens the console application , as shown in the figure.
5 >> add code to creating the application :
showing application hello world :
using System;
using System.Collection.Generic;
using System. Linq;
using system.text;
using system.threading.tasks;
namespace helloworld
{
class program
{
puvblic static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("hello world");
console.RedKey();
}
}
}
puvblic static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("hello world");
console.RedKey();
}
}
}
shows a stander-ed C# application that prints the literal string hello world to the console output window.
In this application , you can see that the entire program is wrapped in the namespace helloworld statement. this namespace contain a class name program , which turn contains a method called main() . The main() method must be declared as static , as it does not require any object foe calling .
run the application by pressing F5 key . the output the application is shown in figure .
CLASS 2 WILL BE CONTINUE TOMORROW TILL THEN SEEYAAAaaaa....!!!!!!
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
 FROSTBOX
FROSTBOX
-
 run iOS theme on windows 7 or 8....
run iOS theme on windows 7 or 8....
-
PERFORMING COMMON TASK IN WEB BROWSER
-
 introduce the new visual studio 2012
introduce the new visual studio 2012
-
LEARN C-SHARP IDENTIFIERS AND KEYWORDS , DATA TYPE , VARIABLES , CONSTANTS ( class 2)
-
THE EASIEST WAY TO DO "E-FILING" (INDIA )
-
 online preparing for aptitude or interview......:)
online preparing for aptitude or interview......:)
-
 LET'S LEARN C-sharp 5.0 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE ( class 1)
LET'S LEARN C-sharp 5.0 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE ( class 1)
-
 THE NEW GOOGLE NEXUS 7
THE NEW GOOGLE NEXUS 7
-
EXCEPTION HANDLING BY USING try....catch...finally statements